How to Use and Optimize Xml Sitemap for Better Indexing
Optimize xml sitemap to make your website easy for Google to understand and show in search results. Think of your XML sitemap like a map of your website. Keep it updated with your best pages, use tools to create it, and make sure you tell Google about it through Google Search Console. Also, don’t include pages you don’t want to show up in search results.
XML sitemaps are a crucial aspect of website structure and search engine optimization (SEO). They provide search engines with a roadmap of the content on a website, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index the site’s pages. However, simply having an XML sitemap is not enough to ensure that a website is being properly indexed.
We will cover the structure of an XML sitemap, how to generate a sitemap, and best practices for optimizing it. Additionally, the article will discuss the importance of regularly updating and submitting a sitemap, as well as utilizing sitemap tools and resources for measuring and analyzing its performance.
By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of how to effectively utilize XML sitemaps for their website’s SEO.
Key Takeaways
- XML sitemap indexing is crucial for a website’s SEO performance and visibility
- Regularly updating and submitting a sitemap to search engines is essential for maximizing SEO potential
- Sitemap tracking and analysis provide valuable insights into how search engines crawl and index a website, allowing for optimization
- Optimizing a sitemap can improve a website’s visibility, attract more organic traffic, and ultimately support SEO efforts.
What is an XML Sitemap?
An XML Sitemap is a structured file that contains information about a website’s pages, designed to help search engines crawl and index the site more efficiently. It is an essential tool for webmasters and online businesses that want to improve their website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs).
XML Sitemaps allow search engines to quickly and easily identify and index the pages on a website, which can ultimately lead to increased traffic and visibility.
One of the primary benefits of using XML Sitemaps is that they provide a comprehensive overview of a website’s structure and content. This makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index the site, as they don’t have to rely solely on crawling the website’s internal links.
Additionally, XML Sitemaps can help webmasters identify and rectify any issues with their website’s structure or content, such as broken links or missing pages. Overall, implementing an XML Sitemap is an important step towards ensuring that a website is fully optimized for search engine rankings.
The Importance of Sitemap Indexing for SEO
The significance of incorporating a sitemap index in SEO strategy cannot be overstated. While content optimization is crucial for improving search engine rankings, sitemap indexing plays a significant role in ensuring that search engines can access and crawl all the pages on a website.
Here are five reasons why sitemap indexing is essential for SEO:
- A sitemap index organizes a website’s URLs into a hierarchical structure, making it easier for search engines to understand how the pages are related to one another.
- Sitemap indexing helps search engines discover new content on a website quickly, allowing it to be indexed and ranked faster.
- Sitemap indexing can help identify and fix crawling errors on a website, improving the website’s overall SEO performance.
- Without proper sitemap indexing, search engines may overlook important pages on a website, resulting in lower rankings and less traffic.
- Properly structured sitemap indexes can also provide additional metadata to search engines, such as how often pages are updated and how important they are to the website.
However, it’s essential to note that sitemap indexing is not a substitute for content optimization. While it can help search engines discover and crawl pages on a website, the quality and relevance of the content still play a critical role in determining search engine rankings.
Additionally, sitemap errors can have a significant impact on SEO, as search engines may be unable to crawl pages if they encounter errors in the sitemap index. Therefore, it’s essential to ensure that sitemap indexes are structured correctly and regularly checked for errors to avoid any negative impact on SEO performance.
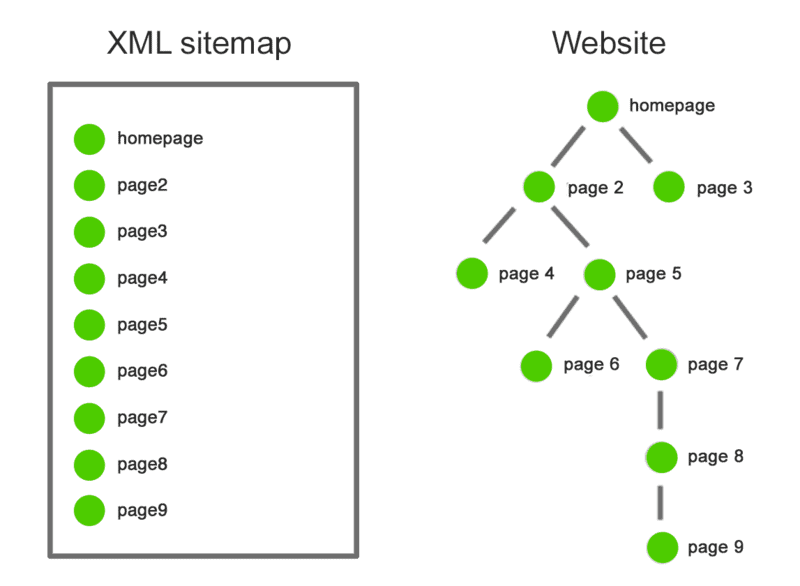
Understanding the Structure of an XML Sitemap
By examining the structure of XML sitemaps, web developers can gain a deeper understanding of how search engines crawl and index their websites. XML sitemaps are designed to provide a roadmap of a website’s content to search engines, making it easier for them to crawl and index all relevant pages. The structure of an XML sitemap is relatively simple, consisting of a root element that contains a series of nested sub-elements.
Each sub-element represents a specific URL on the website, and contains information about the page’s last modification date, its priority relative to other pages on the site, and the frequency with which it is expected to change. By providing this information in a consistent and structured format, XML sitemaps enable search engines to more efficiently crawl and index a website’s content. However, in order to maximize the benefits of XML sitemap indexing, developers must also be familiar with parsing techniques that allow them to quickly and accurately extract information from these files.
To illustrate the structure of an XML sitemap, consider the following table:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| urlset | The root element of the XML sitemap |
| url | A sub-element representing a specific URL on the website |
| loc | The URL of the page |
| lastmod | The date the page was last modified |
| changefreq | The expected frequency of page updates |
By understanding the different elements and sub-elements that make up an XML sitemap, web developers can optimize their website’s indexing and improve its visibility in search engine results pages. Additionally, by employing parsing techniques that enable them to quickly and accurately extract information from these files, developers can make updates and changes to their website’s content more efficiently and effectively.
How to Generate a Sitemap for Your Website
To generate a sitemap for a website, one can use various online tools and plugins that automatically crawl the website and create a structured list of URLs. These tools are designed to simplify the process of generating sitemap templates, and they can be used even by individuals without technical expertise.
Additionally, there are manual methods that can be used to create a sitemap, but they require a bit more effort and technical knowledge.
Once the sitemap has been generated, the next step is to submit it to various search engines. This can be done via the search engine’s webmaster tools or by simply adding the sitemap URL to the robots.txt file.
It is important to ensure that the sitemap is updated regularly, especially when new content is added to the website. By following these sitemap submission strategies, website owners can improve the indexing and ranking of their website on search engine results pages.
Best Practices for Optimizing Your Sitemap
Applying effective optimization techniques to a sitemap can significantly improve a website’s visibility and accessibility to search engines. One of the most important sitemap optimization techniques is to ensure that the sitemap is properly structured and formatted. This includes organizing URLs by priority, updating the sitemap regularly, and ensuring that the sitemap adheres to search engine guidelines.
Another important aspect of sitemap optimization is submitting the sitemap to search engines through various sitemap submission strategies. These strategies include submitting the sitemap through the search engine’s webmaster tools, using a ping service to notify search engines of updates, and incorporating the sitemap URL into the website’s robots.txt file.
By utilizing these submission strategies, website owners can ensure that their sitemap is fully indexed by search engines, which can lead to improved search engine rankings and increased website traffic.
Including Important Pages and Information
Including essential pages and relevant information in a sitemap is crucial for facilitating search engines to properly crawl and understand a website’s content. Maximizing crawlability is important for creating a comprehensive sitemap that enables search engines to access all pages on a website. This can be achieved by including all important pages in the sitemap, including categories, tags, and subpages.
Additionally, the sitemap should prioritize the pages that are most important to the website’s overall SEO goals. Sitemap prioritization is an essential aspect of optimizing XML sitemaps. Prioritizing pages in the sitemap can ensure that search engines crawl the most important pages first, which can help those pages rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The prioritization of pages in the sitemap can be achieved by using the ‘priority’ tag. The priority tag assigns a relative priority to each page in the sitemap, with the most important pages receiving a higher priority score. By prioritizing pages, website owners can ensure that search engines crawl the right pages first, which can improve the overall SEO of a website.
Updating and Submitting Your Sitemap
One crucial step in the process of maximizing a website’s SEO potential is regularly updating and submitting its sitemap to search engines. Sitemap tracking allows website owners to monitor search engine crawlers’ behavior when indexing their website. This information helps website owners identify any issues with their sitemap and take necessary measures to improve their website’s indexing and ranking.
XML submission is an essential aspect of sitemap tracking. Search engines, such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo, use XML sitemaps to crawl and index websites efficiently. By submitting an updated XML sitemap to these search engines, website owners can increase their chances of being indexed promptly and accurately.
Additionally, regularly submitting an XML sitemap helps search engines prioritize website content, leading to better visibility and higher search rankings.
Utilizing Sitemap Tools and Resources
After updating and submitting your sitemap, the next step to ensure its effectiveness is to conduct a sitemap analysis. This process involves evaluating the sitemap’s content, structure, and URLs to ensure they are all functioning correctly. Sitemap analysis provides valuable insights into how search engines crawl and index your site, allowing you to optimize your sitemap for better indexing.
To aid in sitemap analysis and optimization, there are various sitemap tools and resources available. These tools can help you identify errors, check for duplicate content, and even generate sitemaps automatically. Some of the most popular sitemap tools and resources include:
- Google Search Console: This free tool from Google provides valuable insights into how your site is performing in search results, including sitemap indexing status and errors.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: This tool crawls your site and analyzes its URLs, providing invaluable insights into potential sitemap issues such as broken links, missing pages, and duplicate content.
- XML Sitemap Generator: This online tool generates XML sitemaps for your site, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content.
By utilizing these sitemap tools and resources, you can improve your sitemap submission strategies and ensure your site is being crawled and indexed effectively.
Measuring and Analyzing Your Sitemap’s Performance
To effectively evaluate the performance of your sitemap, it is essential to analyze its metrics and identify areas for improvement.
One way to track metrics is to use tools like Google Search Console, which provides valuable insights into how your sitemap is being crawled and indexed by search engines. By regularly monitoring the search console, you can quickly identify any crawl errors and take the necessary steps to fix them.
For example, if you notice that some URLs are not being indexed, you can check the URLs for errors, such as broken links or incorrect formatting, and fix them.
Another critical metric to track is the number of pages that are being indexed. If you notice that your sitemap is not being fully indexed, you may need to adjust your sitemap’s structure or content to improve its visibility to search engines.
Additionally, analyzing user behavior metrics, such as bounce rate and time on page, can provide insights into how users are interacting with your sitemap and help you identify areas that need improvement.
Overall, by regularly monitoring and analyzing your sitemap’s metrics, you can identify and address any issues that may be hindering its performance and ensure that it is effectively supporting your website’s SEO efforts.
Measuring and analyzing your sitemap’s performance is crucial to ensuring that it is optimized for search engines and effectively supporting your website’s SEO efforts. By tracking metrics, identifying crawl errors, and analyzing user behavior, you can identify areas for improvement and take the necessary steps to optimize your sitemap’s performance.
With a well-optimized sitemap, you can improve your website’s visibility, attract more organic traffic, and ultimately achieve your SEO goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all search engines support XML sitemap indexing?
XML sitemap indexing offers several advantages, including improved crawling and indexing of a website’s pages. It is important to validate XML sitemaps to ensure search engines can correctly interpret them. While most search engines support XML sitemap indexing, it is recommended to check with specific search engines for their compatibility.
Can I include URLs from other domains in my XML sitemap?
It is generally not recommended to include cross domain URLs in an XML sitemap, as it may not be crawled or indexed properly by search engines. Best practices suggest keeping the sitemap focused on URLs within the same domain.
Is there a limit to the number of URLs that can be included in an XML sitemap?
The number of URLs that can be included in an XML sitemap is not officially limited, but Sitemap optimization is necessary to ensure crawling efficiency. Large sitemaps may be split into smaller files and compressed for faster indexing.
Should I include canonical tags in my XML sitemap?
Including canonical tags in an XML sitemap can have benefits in terms of canonicalization, reducing the impact of duplicate URLs and improving overall site structure. However, it is not necessary for all websites and should be implemented strategically.
How often should I update my XML sitemap?
Frequent updating of an XML sitemap optimizes crawl rate and enhances the benefits of sitemap updates. Regular updates ensure that search engines crawl the latest versions of web pages, improving their visibility and ranking.







